第一章 单元测试
1、单选题:
A ( ) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing, and displaying geospatial data.
选项:
A:Global Navigation Satellite Systems(GNSS)
B:Geographic Information System (GIS)
C:Remote Sensing (RS)
D:Global Positioning System(GPS)
答案: 【Geographic Information System (GIS)】
2、单选题:
( ) explicitly expresses the spatial relationships between features, such as two lines meeting perfectly at a point.
选项:
A:Polygons
B:Raster data
C:Topology
D:Vector data
答案: 【Topology】
3、单选题:
The raster data model uses ( ) to represent spatial features.
选项:
A:Point features
B:Line features
C:A grid and grid cells
D:Polygon features
答案: 【A grid and grid cells】
4、多选题:
The vector data model uses ( ) to represent spatial features with a clear spatial location and boundary.
选项:
A:Polygons
B:Lines
C:Pixels
D:Points
答案: 【Polygons ;
Lines ;
Points】
5、多选题:
The most expensive part of a GIS project is data acquisition, and two basic options for data acquisition are ( ).
选项:
A:Scanning
B:Use existing data
C:Create new data
D:Manual digitizing
答案: 【Use existing data;
Create new data】
6、判断题:
Feature-based query can involve either attribute or spatial data. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【对】
7、判断题:
Buffering combines geometries and attributes from different layers to create the output. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【错】
8、判断题:
GIS models can be grouped into four general types: binary model,index model,regression model,and mathematic model. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【错】
9、判断题:
A zonal operation of raster data analysis operates on a group of cells with same values or like features. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【对】
10、判断题:
A process model integrates existing knowledge about the environmental processes in the real world and quantifies the processes with a set of relationships and equations. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【对】
第二章 单元测试
1、单选题:
A ( )is a mathematical model of the Earth, which serves as the reference or base for calculating the geographic coordinates of a location.
选项:
A:spheroid
B:datum
C:geodetic coordinates
D:geoid
答案: 【datum】
2、单选题:
( ),an even closer approximation of the Earth, has an irregular surface, which is affected by irregularities in the density of the Earth’s crust and mantle.
选项:
A:Spheroid
B:Mean sea level
C:Datum
D:The geoid
答案: 【The geoid】
3、多选题:
Which following projections are conformal projections? ( )
选项:
A:Albers equal-area conic projection
B:Mercator projection
C:Lambert conformal conic projection
D:Transverse Mercator projection
答案: 【Mercator projection ;
Lambert conformal conic projection ;
Transverse Mercator projection】
4、多选题:
Which following characteristics belong to Transverse Mercator projection ? ( )
选项:
A:Use standard meridian
B:Conformal
C:No length distortion on standard meridian
D:An equivalent projection
答案: 【Use standard meridian;
Conformal;
No length distortion on standard meridian】
5、单选题:
5If I want to preserve direction during projection, I need to choose ( ) map projection.
选项:
A:Equidistant
B:Conformal projection
C:Azimuthal projection
D:Equivalent projection
答案: 【Azimuthal projection】
6、判断题:
The principal scale applies only to the standard line in a map projection. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【对】
7、判断题:
The projection you choose significantly affects the properties of a large-scale map but has less effect on the properties of a small-scale map. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【错】
8、判断题:
8A map projection allows us to work with longitude and latitude values rather plane coordinates. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【错】
9、判断题:
9A standard line refers to the line of tangency between the projection surface and the reference globe, including standard parallel and standard meridian. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【对】
10、判断题:
The origin of local datum is at the center of the Earth. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【错】
第三章 单元测试
1、单选题:
The ( ) of a raster refers to the number of bits for storing cell values, a higher ( ) means that the cell can store a wider range of values.
选项:
A:Cell size
B:Cell depth
C:Raster format
D:Raster pixels
答案: 【
2、单选题:
The cell ( ) is the size of the area represented by a single cell.
选项:
A:depth
B:size
C:range
D:values
答案: 【】
3、单选题:
Which procedure converts vector data to raster data? ( )
选项:
A:Automatic Vectorization
B:Digitization
C:Interactive Tracing
D:Rasterization
答案: 【
4、多选题:
The spatial data could come from ( )。
选项:
A:X-Y Coordinates
B:Digital data
C:Paper maps
D:GPS / Remote Sensing
答案: 【
5、多选题:
Which of the following events belong to the continuous view of spatial phenomena ( )。
选项:
A:temperature
B:epicentres of earthquakes
C:elevation
D:soil characteristics
答案: 【】
6、判断题:
Connectivity, adjacency, and containment are topologic relationships. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
7、判断题:
The three basic steps of vectorization include line thinning, line extraction, and topological reconstruction. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
8、判断题:
Topological relationships between spatial features allow GIS users to perform spatial data query. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
9、判断题:
Manual digitizing is similar to heads-up digitizing in the way the lines have to be traced by hand, but it works directly on the computer screen using the scanned raster image as background. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 】
10、判断题:
A wide variety of data used in geographic information systems(GIS) are encoded in vector format. They include digital elevation data, satellite images, digital orthophotos, scanned maps, and graphic files. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
第四章 单元测试
1、单选题:
( )marked the beginning of the acquisition of aerial photography on a routine basis.
选项:
A:In 1909
B:World War I
C:Early 1800s
D:Satellite Remote Sensing
答案: 【
2、单选题:
( )is the first of many Earth-orbiting satellites designed for observation of the Earth’s land areas.
选项:
A:Landsat 1
B:SPOT
C:IKONOS
D:QUICKBIRD
答案: 【
3、多选题:
The three most important contributions of Landsat Satellites include ( ).
选项:
A:To create an incentive for the rapid and broad expansion of uses of digital analysis for remote sensing.
B:Its role as a model for development of other land observation satellites designed and operated by diverse organizations throughout the world.
C:The routine availability of multispectral data for large regions of the Earth’s surface.
D:One example of hyperspectral remote sensing
答案: 【】
4、多选题:
According to the platform, remote sensing can be classified as ( )。
选项:
A:Space Remote Sensing
B:Microwave Remote Sensing
C:Terrestrial Remote Sensing
D:Airborne Remote Sensing
答案: 【】
5、多选题:
( )belong to active remote sensing.
选项:
A:LiDAR.
B:SONAR
C:Sunlight photography
D:Flash photograph
答案: 【】
6、判断题:
According to the application field, remote sensing could be classified as agriculture remote sensing, forestry remote sensing, atmospheric Remote Sensing, oceanographical Remote Sensing, geological remote sensing, and military remote sensing and so on. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
7、判断题:
During World War I, use of the electromagnetic spectrum was extended from the visible spectrum to other regions, most notably the infrared and microwave regions. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
8、判断题:
By December 1999, NASA had launched Terra-1, the first satellite of a system (Earth Observation System, EOS) specifically designed to acquire global coverage to monitor changes in the nature and extent of Earth’s ecosystems. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
9、判断题:
Active remote sensing employs instruments designed to sense energy emitted by the Earth, not energy generated by a sensor. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
10、判断题:
Remote Sensing refers to the practice of deriving information about the Earth’s land and water surfaces using images acquired from an overhead perspective, using electromagnetic radiation in one or more regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, reflected or emitted from the Earth’s surface. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
第五章 单元测试
1、单选题:
What is the most possible emissivity for a blackbody of 4000K? ( )
选项:
A:0.8
B:0.5
C:1
D:0
答案: 【】
2、单选题:
Each of the three subtractive primaries absorbs ( )of the visible spectrum.
选项:
A:All
B:Half
C:Two thirds
D:one third
答案: 【】
3、单选题:
By physically moving the object, the kinetic energy of the object is transferred from one place to another. This kind of energy transfer is ( )。
选项:
A:Conduction
B:Convection
C:Transfer
D:Radiation
答案: 【】
4、单选题:
Which gas is responsible for the most absorption of solar radiation? ( )
选项:
A:N2
B:H2O
C:O3
D:CO2
答案: 【】
5、单选题:
Which term describes the energy emitted from a unit area? ( )
选项:
A:Radiant exitance
B:Radiant flux
C:Radiation
D:Irradiance
答案: 【
6、判断题:
Conduction is the only form of energy transfer that can take place in a vacuum. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
7、判断题:
The emissivity of a true blackbody is 0, and that of a whitebody would be 1. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
8、判断题:
Near infrared radiation is solar radiation reflected from the Earth’s surface, and is called reflective infrared. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
9、判断题:
As blackbodies become hotter, the wavelength of maximum emittance shifts to shorter wavelengths. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
10、判断题:
Those wavelengths of electromagnetic radiations that are relatively easily transmitted through the atmosphere are referred to as atmospheric windows. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
第六章 单元测试
1、单选题:
If the nominal spatial resolution of the pan band of a remotely sensed imagery is 30 m, what is the most possible nominal spatial resolution of the multispectral bands of the imagery? ( )
选项:
A:10 m
B:20 m
C:30 m
D:50 m
答案: 【】
2、单选题:
The radiometric resolution of HRVIR sensor carried by SPOT-4 is 8 bit, how many tone levels does the HRVIR imagery have? ( )
选项:
A:512
B:256
C:2048
D:1024
答案: 【】
3、单选题:
Which data source belongs to active remote sensing? ( )
选项:
A:Quickbird imagery
B:RADAR
C:Orthophoto
D:IKONOS
答案: 【
4、单选题:
( )was launched in 1972 as the first satellite tailored specifically for broad-scale observation of the Earth’s land areas.
选项:
A:SPOT
B:MODIS
C:Landsat
D:QuickBird
答案: 【
5、多选题:
Spectral resolution refers to the ( ) in electromagnetic spectrum to which a remote sensing instrument is sensitive.
选项:
A:Frequency
B:band location
C:The size of bandwidth
D:The number of bandwidth
答案: 【】
6、判断题:
Image tone is the frequency of tonal change on an image, or the apparent roughness or smoothness of an image region. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
7、判断题:
Geostationary orbit that is designed to reduce variations in illumination by systematically moving (precessing) the orbital track such that it moves westward 360° each year. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
8、判断题:
If we resample an image of 30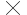 30 m to 15
30 m to 15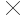 15 m, we improve the spatial resolution of the image. ( )
15 m, we improve the spatial resolution of the image. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
9、判断题:
For digital imaging system, the resolving power of digital imaging system depends on instantaneous field of view (IFOV) and ground sampled distance (GSD). ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】
10、判断题:
The geostationary sensors are stationary to the Earth and always stare at the same location on the Earth surface, so, the temporal resolution is meaningless to the design of geostationary satellites. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
第七章 单元测试
1、单选题:
Which is NOT one of the components of GPS ? ( )
选项:
A:Control component
B:Mechanic component
C:User component
D:Space component
答案: 【
2、单选题:
At least ( ) satellites are required to calculate the distance from the satellite to the receiver.
选项:
A:Five
B:Three
C:Six
D:Four
答案: 【】
3、多选题:
The natural errors that cause GPS errors include ( )。
选项:
A:ionospheric refraction
B:multipath
C:receiver noise
D:tropospheric refraction
答案: 【】
4、多选题:
( ) are the three basic codes in GPS.
选项:
A:P(Y)-code
B:Navigation code
C:Normal code
D:C/A code
答案: 【】
5、多选题:
GPS is a dual-use system and carries two services, including ( )。
选项:
A:Precise positioning service
B:Standard position service
C:Authorized service
D:Open service
答案: 【】
6、判断题:
The space segment of GPS consists nominally of 24 satellites operating in six orbital planes spaced at 60° intervals around the equator. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
7、判断题:
For differential GPS(DGPS), base is on unknown point and rover is on known point. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
8、判断题:
The first BeiDou system (Beidou-1) consists of 35 satellites, including 5 geosynchronous satellites and 30 earth orbiting satellites. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
9、判断题:
Because of the clock biases and other sources of error, the observed range from the satellite to receiver is not the true range, and thus it is called a pseudorange. ( )
选项:
A:对
B:错
答案: 【】
10、判断题:
GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and compass (or Beidou) are four global navigation satellite systems in the world nowadays. ( )
选项:
A:错
B:对
答案: 【】


请先 !